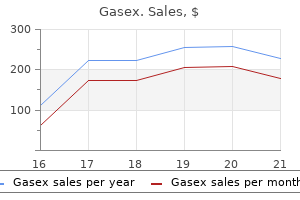
Gasex
Rebecca S. Uranga, MD
- Resident, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Dartmouth-Hitchcock
- Medical Center, Lebanon, New Hampshire
Gasex dosages: 100 caps
Gasex packs: 1 bottle, 2 bottle, 3 bottle, 4 bottle, 5 bottle, 6 bottle, 7 bottle, 8 bottle, 9 bottle, 10 bottle

Order gasex 100caps on line
Arrhythmia in these sufferers is usually caused by progressive gastritis symptoms toddler buy gasex 100 caps amex, abnormal hemodynamics resulting in gastritis diet åõ cheap gasex 100caps on-line chamber dilatation and/or hypertrophy with resultant ventricular dysfunction gastritis diet brat order 100caps gasex fast delivery. D, Department of Radiology, Stanford University School of Medicine, pathologic specimen photographs from Diane Spicer, B. Anatomic correction of transposition of the nice arteries with ventricular septal defect. Half-turned truncal switch operation for full transposition of the great arteries with ventricular septal defect and pulmonary stenosis. Surgical results in patients with double outlet proper ventricle: a 20-year experience. Biventricular repair in double outlet right ventricle: surgical results based on the sts-eacts worldwide nomenclature classification. Clinical outcomes of arterial swap operation for double-outlet right ventricle with subpulmonary vsd. Biventricular restore of double outlet right ventricle with non-committed ventricular septal defect (vsd) by vsd rerouting to the pulmonary artery and arterial switch. Determinants of repair kind, reintervention, and mortality in 393 youngsters with double-outlet right ventricle. Early and late results after correction for double-outlet right ventricle: uni- and multivariate analysis of risk components. Canadian Cardiovascular Society Consensus Conference Guidelines on Heart Failure, replace 2009: analysis and administration of right-sided coronary heart failure, myocarditis, gadget therapy and up to date necessary medical trials. Ventricular arrhythmias after correction of ventricular septal defects: significance of surgical method. Pregnancy after undergoing the fontan process for a double outlet proper ventricle: report of a case. The conduction system in double outlet right ventricle with subpulmonic ventricular septal defect and related hearts (the taussigbing group). Surgical anatomy of double-outlet right ventricle with situs solitus and atrioventricular concordance. Cross sectional echocardiographic findings, their anatomical explanation, and surgical relevance. Demonstration of coronary arteries and main cardiac vascular buildings in congenital coronary heart 28. Mr anatomy of ventricular septal defect in double-outlet right ventricle with situs solitus and atrioventricular concordance. Conotruncal anomalies in fetal life: accuracy of diagnosis, associated defects and end result. Incomplete transposition of the good vessels with biventricular origin of the pulmonary artery (raussig-bing complex); report of 4 circumstances and review of the literature. Surgical treatment of origin of each vessels from proper ventricle, together with cases of pulmonary stenosis. Intraventricular rerouting of blood for the correction of taussig-bing malformation. An operation for double-outlet proper ventricle with transposition of the great arteries. Intraventricular tunnel repair for taussig-bing heart and associated cardiac anomalies. Anatomic restore of anomalies of ventriculoarterial connection associated with ventricular septal defect. Surgical correction of double-outlet right ventricule with noncommitted ventricular septal defect. Surgical approaches for double-outlet proper ventricle or transposition of the nice arteries related to straddling atrioventricular valves. A new surgical restore for transposition of the nice arteries associated with ventricular septal defect and pulmonary stenosis. As a outcome, the potential exists for confusion and misunderstanding both between and within institutions. Terms which have been used to describe this group of hearts embrace single ventricle, univentricular coronary heart, frequent ventricle and, more just lately, single practical ventricle. The trabecular portion exists between the inlet and outlet portions and consists of the ventricular apex. But, in a morphologic proper ventricle, the inlet and outlet portions are separated from one another by the cnsta supraventricularis. Their last remark that they primarily based their definition of a ventricle on was that within the normal coronary heart, each trabecular zone receives its own inlet. Rudimentary chambers consisting of an outlet portion have been categorized further as an "outlet chamber. Two are biventricular (concordance and discordance), one is ambiguous (in cases of atrial isomerism), and three are univentricular (double inlet, single inlet, and common inlet). Patients with any type of single useful ventricle are amenable to a modified Fontan kind of surgical restore. We will use the time period "single useful ventricle" to help avoid any conceptual confusion that phrases like "univentricular coronary heart" and "single ventricle" might cause. In this anomaly, the rudimentary proper ventricle is situated anterior and superior to the dominant left ventricular chamber and mostly connects to the ascending aorta (ventriculoarterial discordance). In this condition, the hypoplastic left ventricular chamber shall be positioned along the inferior (diaphragmatic) facet of th. Consequently, the ventriculoarterial connections are virtually all the time proper ventricular and could additionally be double outlet, widespread outlet (truncus arteriosus), or single outlet (with pulmonary or aortic atresia). Rarely, the morphology of neither the dominant chamber nor the hypoplastic chamber can be determined with certainty. Schematic illustrating three basic forms of univentricular connection: double inlet, single inlet, and common inlet. The valve that straddles is nearly at all times on the same side as the hypoplastic outlet chamber. Note the related impact of accelerating atrial and ventricular septal malalignment produced by increasing annular override. Ventricular Arterial Connections In univentricular coronary heart, any ventriculoarterial connection can happen, including concordant connection. A: the sequence of anomalies that hyperlink the different varieties of double-inlet ventricles with the traditional heart when there has been right-hand (d) embryonic ventricular looping. B: the comparable collection of double-inlet ventricles when there has been left-hand (I) embryonic ventricular looping. Similar to the conventional two-ventricle coronary heart, the ventriculoarterial relationship is defined by the ventricle from which most (>50%) of an overriding semilunar valve originates. The outlet foramen often could be restrictive, occurring in 47% of instances within the sequence revealed by Bevilacqua et al. The defect may be restrictive or unrestrictive at start but usually will turn into restrictive over time. In the setting of univentricular coronary heart of left ventricular morphology, the majority of sufferers may have discordant ventriculoarterial connections, with the aorta arising from the rudimentary outlet chamber of right ventricular morphology, and the pulmonary artery arising from the dominant ventricular mass of left ventricular morphology. For the rest of the patients of their collection, 23 % were discovered to have transposition of the great arteries of the n-loop selection.
Discount gasex 100caps otc
These methods include dosage discount of calcineurin inhibitors and the usage of antiproliferative brokers like sirolimus and everolimus (154 gastritis diet óçáåê discount gasex 100caps with amex,225 gastritis symptoms heartburn buy discount gasex 100 caps line,226) diet with gastritis recipes cheap gasex 100caps with mastercard. A excessive prevalence of lipoprotein abnormalities has been described amongst pediatric heart transplant recipients (227). Again, the use of cyclosporine and steroids has been related to this disorder. Therefore, the growing use of lipidlowering brokers also in pediatric patients seems justified. Posttransplant diabetes mellitus is current in roughly 2 % of pediatric recipients with cyclosporine-based immunosuppression, but in 8% of recipients with tacrolimus-based immunosuppression (228, 229). Sirolimus reportedly has less nephrotoxicity than cyclosporine or tacrolimus but has been related to severe stomatitis and frequent elevations in ldl cholesterol and lipid profiles (233). Of these, as many as 20% will develop coarctation of the aorta that will require treatment. Although surgical repair could also be essential in advanced obstructive lesions, balloon coarctation angioplasty is a protected and efficient remedy in most conditions (234) (see Chapter 13). Severe tricuspid regurgitation secondary to valve damage from endomyocardial biopsies is an unusual however doubtlessly hemodynamically significant complication. Attempts to minimize the number of biopsies, cautious placement of the biopsy catheter, or the utilization of a protracted sheath may cut back the incidence of this complication. Intermediate outcome is much like that of kids present process main heart transplantation (236,237). When retransplantation is carried out in the setting of early major graft failure, the results are quite poor and a lot of investigators consider retransplantation on this setting inappropriate (237,238). Encouragingly, the outcomes following retransplantation after a protracted intertransplant interval are equal to the outcomes following major transplant (236). The medical and pharmacologic issues after retransplant mimic these following main transplant. Heterotopic and Heart-Lung Transplantation Experience with heterotopic heart transplantation in kids is limited. The effect of panel reactive antibodies and the donor specific crossmatch on graft survival after coronary heart and heart-lung transplantation. Utilization of intravenous immunoglobulin to ameliorate alloantibodies in a highly sensitized affected person with a cardiac assist gadget awaiting heart transplantation. Pediatr Transplant that precludes orthotopic coronary heart transplantation, though some contemplate availability of an undersized donor or expectation of a certain degree of recipient heart restoration to be indications as properly. One- and five-year actuarial survival rates have been reported to be as high as 83% and 66%, respectively. Thus, in selected patients, heterotopic coronary heart transplantation could additionally be thought-about an alternate, notably when pulmonary vascular resistance is excessively high for orthotopic coronary heart transplantation. The volume of pediatric heartlung transplantation decreased significantly within the 2000s both in frequency and in survival rates (239,240). Thus, the continuing position of this procedure within the administration of irreversible pediatric cardiopulmonary illness remains unsure. In common, the poor late survival after heart-lung transplant tracks the poor late survival seen after lung transplant alone. Another different that has met with some success in the setting of excessively high, fastened pulmonary vascular resistance in these sufferers with unrepaired congenital heart lesions is the efficiency of single-lung transplantation and repair of the congenital coronary heart lesion (30). Cardiac transplantation for neonates with hypoplastic left heart syndrome [editorial; comment]. Predicting end result after itemizing for heart transplantation in youngsters: comparison of Kaplan-Meier and parametric competing risk evaluation. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for bridge to heart transplantation among kids within the United States: evaluation of data from the organ procurement and transplant network and extra corporeal life support organization registry. Indications for heart transplantation in pediatric coronary heart illness: a scientific assertion from the American Heart Association Council on Cardiovascular Disease within the Young; 28. Mortality and morbidity in presensitized pediatric heart transplant recipients with a optimistic donor crossmatch using peri-operative plasmapheresis and cytolytic remedy. Impact of antibodies in opposition to human leukocyte antigens on long-term end result in pediatric coronary heart trans- forty two. Use of bortezomib for prevention and remedy of rejection in sensitized patients. Pediatric lung transplantation for pulmonary hypertension and congenital heart illness. Utility of prostaglandin El in the pretransplantation analysis of coronary heart failure patients with significant pulmonary hypertension [see comments]. Pharmacologic discount of pretransplantation pulmonary vascular resistance predicts consequence after pediatric heart transplantation. Intermediate follow-up of pediatric coronary heart transplant recipients with elevated pulmonary vascular resistance index. Vasodilator remedy after coronary heart transplantation: effects of inhaled nitric oxide and intravenous prostacyclin, prostaglandin El, and sodium nitroprusside. Exercise capability in pediatric coronary heart transplant candidates: is there any position for the 14 mllkg/min guideline A cross-sectional examine of train performance during the first 2 a long time of ljfe after the Fontan operation. Fate of infants with hypoplastic left coronary heart syndrome listed for cardiac transplantation: a multicenter research. Orthotopic heart transplantation for congenital coronary heart disease: another for high-risk fonran candidates Outcome of itemizing for cardiac transplantation for failed Fontan: a multi-institutional examine. Protein-losing enteropathy after Fontan surgical procedure: resolution afrer cardiac transplantation. The impact of age, prognosis, and former surgery in youngsters and adults undergoing heart transplantation for congenital coronary heart disease. Heart transplantation after congenital coronary heart surgical procedure: improving results and future goals. Carvedilol produces dose-related enhancements in left ventricular function and survival in subjects with continual heart failure. Prospective Randomized Evaluation of Carvedilol on Symptoms and Exercise [see comments]. Carvedilol in youngsters with cardiomyopathy: 3-year expertise at a single institution. Use of extracorporeallife help as a bridge to pediatric cardiac transplantation. Pneumatic paracorporeal ventricular help system in infants and kids: initial Stanford experience. Ventricular help system software with the intermediate use of a membrane oxygenator as a bridge to pediatric heart transplantation.
Gasex 100 caps with amex
Several medical parameters have been suggested to help this differential prognosis gastritis diet 17 purchase gasex 100caps visa. In the United States chronic gastritis flatulence cheap gasex 100caps line, customary screening follow dictates that a private and household historical past be obtained and a bodily examination performed gastritis diet in telugu discount gasex 100caps without prescription. Nevertheless, the onset of symptoms and heart failure in infancy or early childhood appears to be an unfavorable prognostic signal indicative of early disease development (87,89,103) with excessive mortality within the ensuing months or years from heart failure, despite aggressive surgical and/or medical remedy. For sufferers first identified in the pediatric age group, correct predictions regarding pure historical past and prognosis are significantly daunting given the significantly lengthy period (>50 years) of potential threat that lies ahead. This is compounded by the truth that most kids who die abruptly have beforehand been asymptomatic (or only mildly symptomatic), and such catastrophes are sometimes the first scientific manifestation of the disease (2,3). There can be frequent association with other congenital heart malformations, the most typical of which is dysplastic pulmonary valve stenosis and atrial septal defect. It is more probably that such rare associations represent solely the sporadic affiliation of two uncommon illnesses rather than constituting an etiologic relationship. Although most patients die whereas sedentary or during normal or modest physical exertion, an essential proportion die all of a sudden during or simply after vigorous exercise. Of notice, although the presence of a subaortic gradient (:2:30 mm Hg at reset) is a robust determinant of progressive coronary heart failure and cardiovascular death. Long-acting preparations of propranolol, atenolo I, metoprolol, or nadolol at the moment are mostly used. In addition, f3-blockers inhibit sympathetic stimulation of the guts and will scale back the outflow gradient underneath circumstances of train and augmented sympathetic stimulation. Sudden deaths in young aggressive athletes: evaluation of 1866 deaths within the United States, 1980-2006. Mild hypertrophy conveys usually lower threat and excessive hypertrophy (wall thickness ~ 30 mm) the best risk. N Engl J Med 2000;342:1778-1785, with permission of Massachusetts Medical Society. Diuretic agents can also be administered judiciously, both alone or at the aspect of either j3-blockers or verapamil, to cut back pulmonary congestion and enhance symptoms. The traditional circumstance occurs in youngsters or adults who experience exertional dyspnea indicative of elevated pulmonary venous pressures, associated with intact or hyperdynamic systolic function. Medical remedy is usually with the aforementioned j3-blockers or calcium antagonist medicine, though either treatment could be administered first. Furthermore, this combination might decrease coronary heart price and/or blood stress excessively. The therapeutic approach to these sufferers is just like that of congestive heart failure in other cardiac ailments, including administration of j3-blockers, angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin-receptor blockers, and diuretics, as nicely as selectively digoxin, spironolactone, and warfarin. Vegetations mostly involve the anterior mitral leaflet or septal endocardium on the web site of mitral valve-septal contact and less generally the aortic valve. The conventional operative process has been the trans aortic septal myectomy (Morrow procedure) by which a portion of muscle is resected from the basal septum (usually about 2 to 5 g). At some centers, the myectomy is prolonged far more distally within the septum (extended myectomy) (129). Results achieved at a number of institutions with this operation over the past 45 years have been glorious, with the overwhelming majority of sufferers afforded substantial symptomatic and hemodynamic benefit (2-5,128-132). Of particular note, recent knowledge from the Mayo Clinic myectomy cohort show that operated patients achieve the identical longevity as the general population and reveal significantly higher survival than nonoperated sufferers with outflow obstruction (129). For example, anomalous papillary muscle insertion instantly into the anterior mitral leaflet (without the interposition of chordat tendinae) produces muscular midventricular obstruction (133,134). This congenital anomaly of the mitral apparatus must be considered prior to intervention since targeted surgical strategy requires distally extended myectomy to relieve obstruction (134). This methodology includes introduction of about 2 ml of 95% alcohol into the primary main septal perforator to produce a transmural myocardial infarction. A virtually equivalent sequence occurred 9 years later, additionally throughout sleep; Patient is now fifty three years old and asymptomatic. Contemporary definitions and classification of the cardiomyopathies: an American Heart Association Scientific Statement from the Council on Clinical Cardiology, Heart Failure and Transplantation Committee; Qualiry of Care and Outcomes Research and Functional Genomics and Translational Biology Interdisciplinary Working Groups; and Council on Epidemiology and Prevention. American College of Cardiology/European Society of Cardiology Clinical Expert Consensus Document on Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Phenotypic spectrum and patterns of left ventricular hypertrophy in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: Morphologic observations and significance as assessed by two-dimensional echocardiography in 600 patients. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy charactenzed by marked hypertrophy of the posterior left ventricular free wall: Significance and medical implications. Heterogeneous morphologic expression of genetically transmitted hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: two-dimensional echocardiogra phic evaluation. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with excessive enhance in left ventricular wall thickness: Functional and morphologic features and clinical significance. Severefunctional limitation in sufferers with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and only mild localized left ventricular hypertrophy. Degree of left ventricular hypertrophy in persistent atrial fibrillation in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Hypertrophic nonobstructive cardiomyopathy with big unfavorable T waves (apical hypertrophy): Ventriculographic and echocardiographic features in 30 patients. Dilemmas in nomenclature characterizing hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and left ventricular hypertrophy. Prevalence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in an outpatient population referred for echocardiographic study. Management implications of massive left ventricular hypertrophy in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy considerably underestimated by echocardiography however recognized by cardiovascular magnetic resonance. Clinical challenges of genotype positive (+)-phenotype unfavorable (-) relations in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Electrocardiographic modifications can precede the event of myocardial hypertrophy within the setting of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Mitral valve abnormalities recognized by cardiovascular magnetic resonance represents a major phenotypic expression of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Quantitative analysis of cardiac muscle cell disorganization within the ventricular septum of sufferers with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Relation between extent of cardiac muscle cell disorganization and left ventricular wall thickness in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Quantitative analysis of cardiac muscle cell disorganization in the ventricular septum. Comparison of fetuses and infants with and with out congenital heart illness and patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Intramural ("small vessel") coronary artery disease in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Pathologic fibrosis and marrix connective tissue in the subaortic myocardium of patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Quantitative evaluation of myocardial fibrosis in normals, hypertensive hearts, and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Cheap 100 caps gasex free shipping
Although the mechanism is unclear gastritis diet amazon gasex 100caps visa, using advanced-age donor hearts (>40 years of age) for appropriately sized teenage recipients carries a significantly larger Lyear posttransplant mortality than use of youthful donor hearts (83) gastritis zeluca discount gasex 100 caps on line. Increasing the number of donors remains an important goal to make sure that sick sufferers in want of transplant have that chance gastritis diet ãóãë purchase gasex 100 caps with amex. Injury to the graft could additionally be acute with hemodynamic dysfunction or more continual manifesting as persistent rejection or graft vasculopathy. Patients with de novo antibodies showing more than 1 12 months following transplantation have the poorest survival (102). Patients with congenital coronary heart disease present unique perioperative issues associated to their particular morphology, previous surgical procedures, and reconstructive surgery. Heart transplantation in youngsters with an anatomic or physiologic single lung has been efficiently carried out, but pulmonary artery reconstruction increases risk for mortality (103-105). Heart transplantation for structural congenital heart disease with single ventricle physiology is associated with substantial early mortality, and transplantation after the acutely failing Fontan may be prohibitively dangerous (53). Fontan standing stays a danger factor of mortality after heart transplantation with an anticipated 5-year survival barely approaching 70%, with particularly increased threat in these with evidence of pulmonary vascular disease (106). Heart transplantation outcomes for patients after the Fontan operation are higher in those that require coronary heart transplantation owing to ventricular dysfunction (rather than those with preserved ventricular perform and failing Fontan circuit) and people without vital comorbidities such as hepatic cirrhosis or persistent malnutrition (57). Protein-losing enteropathy is a extreme complication of Fontan physiology however can be improved by coronary heart transplantation (55,fifty eight,107). Moreover, the long-term destiny of protein-losing enteropathy after heart transplantation has not been utterly elucidated, and recurrence of protein-losing enteropathy after heart transplantation has been reported. This kind of strategy has resulted in improved wait-time survival of infants in some studies, but not in all studies (91,92). Myocardial damage and explanation for death, donor versus recipient size, donor coronary heart ischemic time, blood and tissue compatibility, infectious status of both donor and recipient, recipient prognosis, and recipient clinical and psychosocial conditions might have an result on myocardial performance and postoperative course. The effects of mind injury and demise on myocardial performance have been investigated (81,93). The strategy of mind death results in myocardial dysfunction and is often as a end result of multiple factors: mind dying itself could trigger myocardial dysfunction; the donor reason for dying (sepsis, trauma, etc. Donor ischemic occasions in pediatric heart transplantation have been reported by many centers to improve the postoperative want for inotropic help but to not be a danger issue for I-year mortality (82,94). This practice requires specific consideration to postoperative administration together with particular immunosuppression and transfusion protocols (87-89). These strategies have included plasmapheresis, a process that entails extracorporeal removal and alternative of the whole plasma quantity (containing antibodies in addition to different proteins such as coagulation factors). Plasmapheresis requires placement of a big bore twin lumen catheter in a big central vein. This is often difficult in younger children because of dimension of blood vessels, lack or minimal vascular entry because of venous occlusions from earlier catheters, and/or systemic venous anomalies. Additional Practical Considerations Adequate monitoring of the postoperative heart transplant affected person is crucial. However, steady, direct measurement of pulmonary artery pressures is commonly monitored in pediatric patients, significantly these with elevated pretransplant pulmonary arterial pressures. Perioperative hemodynamic instability could be present and could be a result of a quantity of causes including graft reperfusion damage, inflammatory response after cardiopulmonary bypass, elevated pulmonary vascular resistance, and labile fluid standing. Most sufferers can be supported with catecholamine infusions after transplant surgery and often benefit from an elevated coronary heart price to compensate for diastolic filling abnormalities. Many agents, similar to prostaglandins, prostacyclin, nitroprusside, inhaled nitric oxide, and others have been confirmed to be efficient in these patients (36). Hemodynamic parameters, similar to right-sided filling pressures and functional right ventricular evaluation with echocardiography can be utilized to follow the course of proper ventricular recovery and direct applicable weaning from supportive measures. A preventive remedy with selective vasodilators in addition to the availability of mechanical help gadgets during and after coronary heart transplantation can cut back deleterious results of each transitional pulmonary hypertension and primary graft failure (109). Primary graft failure and early morbidity are largely defined by recipient points that improve perioperative threat (110). Acute renal failure occurs postoperatively in 3% to 10% of transplant recipients (111). Multidisciplinary staff administration including nephrology consultation is usually helpful in this circumstance. Patients usually develop systemic hypertension in the quick postoperative interval. This may be secondary to baroreflex-mediated hypertension, catecholamine dysregulation from low cardiac output earlier than transplant, significant preexisting renal harm, and newly initiated immunosuppressive medicines such as corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors. Treatment consists of antihypertensive medication titration to achieve a normal blood stress for age. An inappropriately small donor coronary heart size has been related to elevated mortality, and a donor/recipient weight ratio <1 has been reported as a major predictor of deadly postoperative heart failure (112). Postoperative pericardial effusions develop in 9% to 21 % of adult recipients (113,114). The incidence in pediatric patients is unknown but is in all probability going much like adults and will, partly, be associated to an increased pericardial quantity created after a dilated heart is changed with normal-sized heart that fills with fluid. Posttransplant sinus node dysfunction is frequent with a reported prevalence as excessive as 44% (115) and is probably going related to myocardial ischemia and surgical manipulation. High-dose corticosteroids are given intraoperatively and continued for a brief time period, after which they are often discontinued or decreased to a low-dose upkeep routine. Over the last 12 years, the incidence of rejection within the 1st year after pediatric coronary heart transplant has decreased from about 60% to just over 40% (119). The peak hazard, or instantaneous threat, for rejection is around 1 to 2 months after transplantation (120). Older age at transplantation represents a threat for first rejection and a risk for an elevated number of episodes of rejection inside the first 6 months after transplantation. Infections happen in up to 25% of pediatric recipients through the early postoperative interval, and 60% of these infections are bacterial (121). Bloodstream and pulmonary infections are most typical, followed by urinary tract and surgical web site infections (123,124). Because of the inconvenience, larger technical challenges, and attainable increased morbidity of biopsy in smaller children, there was a lot interest in evaluating the position of echocardiography in youngsters present process transplantation (125-131). Despite this interest, the controversy over the position of echocardiography is way from resolved. In reality, many facilities have discontinued routine surveillance biopsies after the 1st or 2nd year from transplantation. Many centers perform routine endomyocardial biopsy on infants significantly much less frequently or not at all, as a substitute depending on physical exam and echocardiogram to help in prognosis, and reserve biopsy just for medical indications (136). With any clinical deterioration in the early postoperative interval, evaluation of and treatment for rejection as the potential cause should be thought-about. The want for noninvasive diagnosis of rejection has stimulated the ongoing seek for biohumoral markers, such as B-type natriuretic peptide. Clinical evaluation of rejection is important but can be misleading, notably in pediatric patients in whom infectious points can mimic the presentation of rejection. The characteristic infiltration of the donor coronary heart by lymphocytes leads to the prognosis of rejection on endomyocardial biopsy (141). The overwhelming majority of initial rejection episodes can be successfully reversed by high-dose corticosteroids alone or in conjunction with anti- T-cell antibodies.
Generic gasex 100 caps on line
Because the height strain within the aorta occurs after the height pressure is reached in the left ventricle chronic gastritis gastroparesis purchase gasex 100 caps fast delivery, the Doppler-derived peak instantaneous pressure gradient represents a special physiologic parameter than the catheter-derived peak-to-peak strain gradient (74) gastritis symptoms chest pain discount 100 caps gasex overnight delivery. The mean systolic strain gradient could be calculated from the Doppler spectral profile gastritis rash gasex 100 caps generic, and this correlates pretty properly with the imply strain gradient derived from simultaneous catheter recordings (75,77). Some investigators favor utilizing mean strain gradient to guide scientific choice making (78). The 2006 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force Report Guidelines for the Management of Patients with Valvular Heart Disease (8) recommends the guidelines for grading the severity of aortic stenosis in accordance with the Doppler-derived gradients. Mild stenosis is present when the peak instantaneous gradient is <36 mm Hg (jet velocity three rn/s) or the mean gradient is <25 mm Hg. Moderate stenosis is current when the height instantaneous gradient is between 36 and sixty four mm Hg (jet velocity between three and 4 rn/s) or the imply gradient is between 25 and forty mm Hg. Severe stenosis is current when the peak gradient is >64 mm Hg (jet velocity 4 rn/s) or the mean gradient is >40 mm Hg. All stress gradient estimations rely not only on the severity of the obstruction, but in addition on underlying hemodynamic circumstances, which may vary considerably at different times in the identical patient. States of elevated contractility or stroke volume will end in higher strain gradients than states of decreased contractility or stroke quantity, and for a given stroke quantity, a sooner heart rate (decreased ejection time) ends in a better pressure gradient. The identical affected person may have considerably different gradient measurements throughout common anesthesia as compared to an alert and anxious state. In addition, sufferers with severe obstruction may have abnormally low myocardial systolic efficiency and low cardiac output, resulting in low strain gradients. For this purpose, many clinicians advocate utilizing valve area calculations rather than stress gradient measurements to gauge the severity of obstruction and information administration selections. The following tips classify the diploma of stenosis based mostly on valve space: space >1. Tissue Doppler imaging may be helpful in assessment of diastolic and systolic left ventricular myocardial dysfunction in sufferers with aortic stenosis. The presence of symptoms in patients with preserved ejection fraction has been attributed to diastolic dysfunction, with related elevated filling pressures and increased myocardial stiffness (81). Doming of the valve leaflets (single arrow) and high-velocity jet (double arrows) is demonstrated. Use of tissue Doppler imaging to measure systolic and diastolic mitral annular velocities permits quantification of systolic long-axis operate and diastolic function. In sufferers with aortic stenosis, the ratio of early mitral inflow velocity (E) to early diastolic mitral annular velocity (F) correlates with the left ventricular finish diastolic stress (82), thereby offering a clinically useful noninvasive technique of assessing diastolic dysfunction. Because longitudinally oriented fibers are present within the subendocardial area, and the subendocardium is most vulnerable to ischemia in patients with aortic stenosis, these fibers are at higher danger than the circumferentially oriented fibers (83). Long-axis dysfunction subsequently may be expected to precede transverse axis dysfunction. Angiography of the left ventricle permits analysis of left ventricular cavity dimension and function, aortic valve annulus size, degree of leaflet thickening and cusp mobility, patency and origin of the coronary arteries, and the size and contour of the ascending aorta. Hemodynamic measurements can be used to calculate the effective valve orifice space by the strategy of Gorlin (85). Such measurements have been shown to correlate well with Doppler measurements of the identical parameters (84). Cardiac Catheterization Due to the evolution of noninvasive strategies that precisely diagnose and consider the anatomy and severity of aortic valve stenosis, cardiac catheterization is usually undertaken primarily for the aim of therapeutic balloon valvuloplasty in patients with recognized aortic valve stenosis and noninvasive evidence of severe obstruction. Information obtained from cardiac catheterization has been considered to be the "gold commonplace" to which traditional and emerging noninvasive modalities have been compared. In addition, congenital aortic valve disease encompasses a large spectrum from important infantile aortic stenosis to regular functioning bicuspid aortic valve. Despite the shortage of very long-term intervention-free knowledge, pure history studies have offered important info. Patients who present in infancy with aortic valve stenosis generally have extra severe stenosis and better mortality with or with out treatment (87-89). In distinction, the 25-year survival in patients who had been 2 years of age or larger on the time of authentic enrollment was 85%. An older examine by Campbell (14), printed in 1968, found that the mean age of demise in sufferers with aortic stenosis was 35 years, with 40% mortality by age 30 and 60% mortality by age forty. Over half of the sufferers who died had sudden sudden dying, whereas many of the remaining deaths had been because of progressive congestive coronary heart failure. About half of sudden dying circumstances from aortic stenosis occur during or instantly after train (93). In the present era, kids with aortic stenosis handled by balloon valvuloplasty have an extremely low risk of sudden surprising death (94). Although gentle aortic stenosis could stay delicate for many years (86), development over time is the rule (14,ninety one,95-97). The fee of development may be larger in kids than in adolescents and adults as a result of lack of ability of the valve orifice to improve in proportion to somatic development (98). Outcome is extremely correlated with the preliminary gradient, with these having larger gradients at the time of prognosis creating symptoms, dying, or requiring valve substitute before these with lower gradients (86,91). Patients with fusion of the best and noncoronary cusps are at risk of extra rapid progression of valve dysfunction (99). Although bacterial endocarditis danger is present even in patients with bicuspid aortic valve without stenosis, the incidence of endocarditis is higher in sufferers with more extreme stenosis. P) represents the stress gradient, from which the mean strain gradient during systole can be calculated using planimetry. The aortic valve space (cm-), then, is calculated by taking the square root of the imply stress gradient and multiplying this by forty four. Unfortunately, the calculation of the valve area might not at all times precisely reflect the diploma of obstruction seen clinically. Measurements utilized in calculation of aortic valve area must be made with excessive care and precision, and the calculated aortic valve area ought to be thought-about together with the entire physique of clinical data when formulating management selections. Treatment Medical Treatment and Balloon Valvuloplasty Because development of valve dysfunction is the rule, medical management is essentially expectant, with timing of intervention being the primary focus. Because adult aortic stenosis is a progressive course of that resembles atherosclerosis, the impact of lipid-lowering medical remedy with statins has been studied, but has not been shown to be helpful in curbing the development of aortic valve adjustments (101). In contrast to older adults with aortic stenosis, for whom intervention is really helpful only when signs develop or are thought-about imminent (8,102), indication for intervention in children and adolescents is more liberal. Whereas for older adults 20-year survival is taken into account long-term, in children and adolescents the aim is survival for many many years. In asymptomatic sufferers with severe congenital aortic stenosis, reduction of the obstruction likely reduces the chance of sudden cardiac demise and decreases the extent of refined and progressive myocardial harm and interstitial myocardial fibrosis (91,ninety two,103,104). Although surgical valvotomy may still be performed, balloon valvuloplasty (105) has usually supplanted open surgical valvotomy as preliminary treatment for congenital aortic valve stenosis in infants, youngsters, and adolescents. Both procedures are usually safe and effective in relieving the obstruction (106), however in both case, subsequent progression of stenosis and/or valve regurgitation is anticipated (88,107-112), with valve substitute thought-about to be the eventual definitive treatment.
Purchase gasex 100 caps without prescription
The number of a particular drug depends upon the primary goal of therapy gastritis diet þòþá generic 100caps gasex visa, underlying or associated conditions gastritis diet 21 buy gasex 100 caps line, and whether or not the treatment is acute or continual in nature gastritis diet herbs discount gasex 100 caps on line. One method to classifying vasodilators groups the drug classes according to their major mechanism of motion (Table 79. Another methodology is to group drugs according to their predominant web site of motion (predominately venous, arteriolar, or balanced; Table seventy nine. Depending on the therapeutic targets, one may select an agent that has predominant results on venous capacitance, arteriolar resistance, or both. Thiazide Diuretics Thiazides inhibit sodium and chloride transport in the distal convoluted tubule of the nephron. Hydrochlorothiazide and chlorothiazide are the first medication on this class used in youngsters with heart problems. In this example, they may be utilized in combination with a loop diuretic and/or a potassiumsparing agent. Adverse effects of thiazides embody hypokalemia, hyperuricemia, and hypercalcemia. Nonrenal effects of thiazide diuretics that have been described in older sufferers and adults embody carbohydrate intolerance and antagonistic results on plasma ldl cholesterol and triglycerides. Nitric Oxide-Modifying Drugs Relaxation of vascular clean muscle by medication in this class is mediated by nitric oxide. Nitroglycerin Nitroglycerin relaxes clean muscle within the cardiovascular, respiratory, and gastrointestinal systems. At the standard therapeutic concentrations, the predominant site of motion is the venous vascular bed. Nitroglycerin has been largely changed by different brokers, but is sometimes administered after cardiac surgical procedure. However, higher doses can produce arteriolar dilation with hypotension and reflex tachycardia. Patients with decreased intravascular quantity (low preload) could respond adversely to nitroglycerin because an extra decline in filling strain may significantly scale back cardiac output. Overdose causes hypotension and tachycardia, which reply quickly to a reduction in dose or cessation of the infusion. Inhibition of this phosphodiesterase leads to pulmonary vasodilation and will also improve the efficacy of inhaled nitric oxide (48,68,69). Orally administered sildenafil has been proven to be efficient in treating persistent pulmonary hypertension in newborns and is properly tolerated. The main use of sildenafil in youngsters with cardiac disease is for patients with acute or continual pulmonary hypertension following cardiac surgical procedure. Nitroprusside is often administered to pediatric cardiac surgical patients within the instant postoperative interval. In addition, it may be effective acutely in youngsters with left ventricular dysfunction and low cardiac output. The main adverse results of nitroprusside are a direct extension of its powerful vasodilator exercise. Due to restricted stability and photodegradation, nitroprusside solutions must be freshly ready earlier than use and protected from mild. Phentolamine is a aggressive nonselective antagonist of a-adrenergic receptors that blocks a1- and az-receptors. Blockade of presynaptic az-adrenergic receptors could contribute to the tachycardia and arrhythmias that happen at excessive doses of phentolamine. Administration of phentolamine to sufferers with low cardiac output produces a lower in systemic vascular resistance with a resultant enhance in cardiac output. Although phentolamine is classed as a mixed vasodilator, the results on venous capacitance are minimal compared with other blended vasodilators. Newborns are more sensitive to the unfavorable inotropic effects of calcium channel blockers than are older youngsters, and intravenous administration of calcium channel blockers in infants has been associated with cardiovascular collapse. Calcium channel antagonists are categorized into three major chemical lessons: phenylalkylamines. Nitric oxide plays a central position in the administration of infants with persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (66,67). This agent can be beneficial in the perioperative period for infants and children with pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with congenital coronary heart disease (48). Enalapril and Lisinopril the mechanism of motion, hemodynamics, and medical indications for enalapril and lisinopril are similar to those described above for captopril. Enalapril and lisinopril could be administered as quickly as daily, which can improve compliance compared to captopril. However, based on theoretical issues and outcomes obtained from scientific trials in adults, these agents might show to be helpful within the pediatric population. This effect has been proven experimentally to be helpful in animal models of muscular dystrophy and connective tissue disorders (73,74). Use of these agents in pediatric sufferers with connective tissue disease such as Marfan and Loeys-Dietz syndromes and Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a topic of present investigation. Mild-to-moderate diuresis may happen due to increased renal blood move and decreased aldosterone formation. Captopril is run orally and peak plasma concentrations typically occur 1 to 2 hours after a single oral dose. Approximately 50% is excreted within the urine unchanged, and thus, captopril plasma clearance is decreased in sufferers with impaired renal function. Captopril is used for the treatment of systemic hypertension and congestive heart failure in infants, kids, and adolescents. Less critical reactions embody rash, style impairment, and minor gastrointestinal disturbances. Aldosterone plays an essential function in selling the abnormal collagen manufacturing and interstitial fibrosis that occurs in chronic coronary heart failure. Administration of aldosterone antagonists, such as spironolactone or eplerenone, to grownup patients with heart failure treated with conventional therapy leads to increased diuresis and symptomatic improvement (72,75). It is administered intravenously and produces vasodilation, will increase glomerular filtration price, inhibits renal sodium reabsorption, and promotes diuresis. Despite considerable investigation within the adult inhabitants, the position and efficacy of nesiritide is controversial. Several research in youngsters suggest nesiritide could increase urine output and scale back ranges of neurohormonal markers of coronary heart failure. Some centers use nesiritide acutely for infants with low cardiac output following cardiac surgical procedure and for infants with severely depressed cardiac perform as a outcome of cardiomyopathy (48,seventy six,77). Furthermore, particular person medicine differ with regard to the degree of important ancillary properties corresponding to a-adrenergic receptor blockade, antioxidant exercise, and intrinsic sympathomimetic exercise (81,82). Some facilities administer either thyroxine or triiodothyronine within the postoperative period if thyroid-stimulating hormone is elevated, circulating thyroid hormone ranges are lowered, and the kid has evidence of low cardiac output (78). However, relatively little printed info exists relating to the protection, efficacy, and longterm results of thyroid hormone administration to children within the early postcardiac surgical procedure interval.
Diseases
- Al Gazali Al Talabani syndrome
- Craniofaciocervical osteoglyphic dysplasia
- Der Kaloustian Jarudi Khoury syndrome
- Chitty Hall Baraitser syndrome
- Pulmonary veins stenosis
- Charcot Marie Tooth disease, neuronal, type A
- Chondrodysplasia punctata, brachytelephalangic
- Rhizomelic dysplasia type Patterson Lowry
- Patau syndrome
- 3 methylglutaconyl coa hydratase deficiency
Discount gasex 100caps on line
The obscure and weird indicators and symptoms of cardiac myxomas typically have led to delayed analysis or misdiagnosis in youngsters and adolescents (137) chronic active gastritis definition order gasex 100caps without a prescription. About 80% of pediatric sufferers current with signs of valvular obstruction (137) gastritis diet 900 purchase 100caps gasex with mastercard. Atrial tumors create mitral or tricuspid valve stenosis by a to-and-fro motion by way of the valves (130 gastritis low carb diet order gasex 100caps without prescription,131). Typically, these giant pedunculated tumors advance by way of and impede the atrioventricular valve throughout diastole and are expelled retrogradely into the atrium during systole. Large left atrial myxomas impede pulmonary venous inflow and move throughout the mitral valve, resulting in indicators and signs of pulmonary edema, pulmonary arterial hypertension, and low cardiac output (130,131,155). Ventricular ischemia and dysfunction might develop when cardiac output is considerably impeded (137). Right-sided heart failure and low cardiac output happen when right atrial tumors impede systemic venous inflow and hinder move throughout the tricuspid valve (130-134). Myxomas might mimic neonatal cyanotic coronary heart disease when obstructive right-sided tumors trigger right-to-left shunting on the atrial level (132-135). Sudden death has been reported when massive tumors fully hinder both the mitral or tricuspid valve (132,133). Large calcified tumors have been related to complete valve destruction (136). Semilunar valve obstruction can occur when large myxomas are inferiorly positioned within the atrium and are attached to a long tumor pedicle (156). This permits atrial tumors to prolapse by way of the atrioventricular valve and ventricular outflow tract, leading to diastolic semilunar valve stenosis. Pedunculated ventricular myxomas (157) also can trigger systolic aortic or pulmonary outflow tract obstruction (28,135,136,156,158). Auscultatory findings of left atrial myxomas are according to atrioventricular valve stenosis and insufficiency (130, 131,136). A mid diastolic murmur and low-pitched tumor plop are attribute findings (13 0,131,159); nonetheless, absence of the murmur could happen with extreme obstruction (119). Right atrial tumors have nonspecific systolic and diastolic murmurs mimicking the Ebstein anomaly or tricuspid valve stenosis and regurgitation (130-134). In the neonate, positional signs encompass feeding difficulty and irritability whereas sitting (134). When tumors hinder the semilunar valves, patients skilled symptoms whereas bending forward or lying down, with reduction of symptoms when standing (157). Peripheral emboli happen in >70% of pediatric sufferers with myxomas (137), together with newborns in whom embolization has been reported to have occurred in utero (132). Emboli are associated to fragmentation of tumor substance or embolization of thrombi adherent to the tumor external surface (131,160). As expected, left-sided tumors are related to systemic (161) and right-sided tumors with pulmonary arterial embolization (132,134). Bilateral atrial myxomas have been reported to trigger both pulmonary and systemic arterial emboli (142), and right-sided tumors have been associated with paradoxical emboli in sufferers with atrial septal communications (132,134). Systemic embolization can occlude coronary, pancreatic, thyroid, adrenal, renal, splenic, cerebral, and extremity arteries, resulting in infarction of corresponding tissue (85,142,155,160). Symptoms associated to peripheral emboli may not become obvious till months to years after removal of the first myxoma (139,142,146,160). In patients older than 1 yr, 15 of 65 (23 %) primary cardiac tumors were myxomas. When these tumors happen in neonates and young infants, they typically mimic congenital heart disease (132-135). Their presentation is often enigmatic because of vague constitutional findings (130,131,136,137). Cardiac myxomas are single left atrial tumors in about 75% and single right atrial tumors in about 25% of patients (124,131,136). Myxomas are usually friable, pedunculated, gelatinous, yellowish brown to red lobular tumors (130,131). These tumors may be calcified (130,131,136,138), with a higher incidence of calcification in right-sided tumors (130,132,133,136,138). Rarely, the tumor pedicle is connected to other segments of the atrial septum, atrial free wall, or mitral valve leaflets (131,134,137,139,140). Myxomas can happen as biatrial tumors connected to the fossa ovalis (138,141,142) or as left atrial tumors protruding via the foramen ovale and filling the best atrium (143). These tumors can occur as single proper or left ventricular myxomas (130,131,135,a hundred and forty four,145) or, infrequently, as multiple myxomas occupying completely different areas of the identical heart (130,136,145). Histologically, these benign tumors are composed of cords and strands of cells in a pale, paucicellular myxoid background. Malignant myxomas are rare and are differentiated by elevated mitotic exercise and pleomorphism (139,146-148). However, the malignant potential may not be determined by histologic findings alone, (146,147,149). Other characteristics of malignant predisposition embrace native invasion on the major website, regrowth of the tumor on the authentic website or completely different location, and development of peripheral aneurysms (139,146,147). The potential for recurrence seems to be related to insufficient resection (162-165) or totipotent multicentricity (166). Small embolic myxoma fragments could continue to develop, undergo malignant transformation, and invade and replace the medial arterial wall, leading to aneurysm formation (130,142,146,160). Constitutional symptoms, the third main part of the scientific triad, occur in ~65% of pediatric patients with myxomas (137). Persistent fever, malaise, weight reduction, arthralgias, and myalgias could additionally be present months earlier than tumor diagnosis (130,131,136,137,one hundred forty,161,167). Laboratory research present anemia, thrombocytopenia, elevated sedimentation fee, and elevated gamma globulins. Patients have been identified as having acute rheumatic fever, persistent rheumatic carditis, subacute bacterial endocarditis, septicemia, myocarditis, and other collagen vascular disorders (134-140,159,161,167169). These constitutional findings have been attributed to a diffuse immunologic response to the primary tumor or to tumor emboli (130,134). Recent stories instructed that these systemic abnormalities are secondary to secretion of interleukin-6 and regularly resolve with tumor resection (169-171). Interleukin-6 is related to the synthesis of a number of proteins that contribute to the acute-phase response and corresponding constitutional indicators and symptoms (172). Right ventricular hypertrophy may be due to pulmonary valvar obstruction, pulmonary arterial hypertension secondary to pulmonary emboli, or pulmonary venous hypertension from left atrial tumors (131). The chest radiograph may be regular (134,144) or might demonstrate cardiomegaly with pulmonary edema (130,131, 134,136).
Generic 100caps gasex free shipping
Arterial pulses beneath the coarctation are diminished in amplitude and delayed in timing in contrast with the proximal pulses (pulsus parous et tardus) gastritis diet bland purchase 100caps gasex with amex. Systolic blood stress is elevated proximal to the coarctation gastritis erythema generic gasex 100 caps without prescription, and a systolic strain gradient is present between the arm and leg gastritis diet öööþíôòâó÷þêã gasex 100 caps. Several medical circumstances might make detection of arterial pulse and stress discrepancies tough. First, the coarctation strain gradient may be minimal, typically as a end result of a light coarctation, but also with coronary heart failure and diminished cardiac output or with a large patent ductus arteriosus. Descending aorta move could also be maintained by a right-to-left ductal shunt and, in the presence of a large ventricular septal defect, the perfusion may be well oxygenated and pulsatile. An anomalous proper subclavian artery arises distal to the coarctation in approximately 3% to 4% of instances. In these patients, the arterial pulse and blood strain are identical in the best arm and leg, and discrepancies are detected only in the left arm. In other sufferers, the left subclavian artery arises adjoining to the coarctation, and its orifice could also be stenotic. In such patients, a bounding arterial pulse and elevated systolic stress shall be detected only in the best arm. A systolic thrill could also be palpable in the suprasternal notch, but the presence of a precordial thrill is unusual in isolated coarctation and should elevate suspicion of an associated intra cardiac lesion. If a sturdy collateral system exists, a standard prevalence in older children and adolescents, prominent collateral artery pulsations may be palpable within the intercostal areas and/or between the scapulae posteriorly. When coarctation manifests in infancy, it often presents as a catastrophic sickness. Congestive heart failure and shock often occur all of a sudden as the ductus arteriosus closes. A giant proportion of these infants have coarctation with essential related lesions corresponding to a ventricular septal defect or aortic stenosis. In an infant with extreme coarctation and a large ventricular septal defect, acute heart failure, shock, and acidosis classically develop suddenly around eight to 10 days of life. Multiorgan system failure, notably renal failure and/or necrotizing enterocolitis and death occur rapidly unless definitive medical and surgical interventions are provided immediately. A grade 2-3/6 systolic ejection murmur originating from the coarctation itself is usually best heard on the upper left sternal border, on the base, and within the left interscapular space posteriorly. If the coarctation is extreme, this systolic murmur may be long and spill into diastole. A ventricular septal defect or mitral regurgitation will produce an S1-coincident holosystolic murmur at the decrease left sternal border or apex. Associated mitral stenosis or a large left-to-right ventricular shunt will give rise to a middiastolic rumble on the apex. Information in regards to the presence of a patent ductus arteriosus and the collateral arterial circulation also could additionally be obtained. Three-dimensional floor rendering can present beautiful anatomic detail in these sufferers (34). Left ventricular hypertrophy with pressure may point out the presence of severe valvar or subvalvar aortic stenosis. Right ventricular hypertrophy that persists past infancy could point out the presence of pulmonary hypertension resulting from related lesions, such as a ventricular septal defect or mitral stenosis. Radiologic Features the chest roentgenogram of an toddler with coarctation who presents with congestive heart failure is nonspecific. Pulmonary vascular congestion could additionally be indistinct and passive in nature, associated to left ventricular failure or mitral stenosis with pulmonary venous hypertension, or it could be active and related to increased pulmonary blood move from a large left-to-right shunt. In older kids and adolescents with coarctation of the aorta, the chest roentgenogram typically exhibits regular or only mildly enlarged heart dimension. Immediately below the three sign, the descending aorta could additionally be prominent because of poststenotic dilation. It is attributable to erosion of the inferior surfaces of posterior ribs by dilated and tortuous intercostal arteries. Rib notching may be unilateral if one subclavian artery is stenotic or arises distal to the coarctation. Two-dimensional and Doppler echocardiography is particularly important in evaluating intracardiac lesions that could be related to coarctation. Cardiac Catheterization and Angiography Echocardiography Two-dimensional echocardiography and Doppler research present an correct, noninvasive assessment of coarctation anatomy and physiology in most patients. From the suprasternal long-axis view, typical thoracic coarctation appears as a localized narrowing of the thoracic aorta just beyond the origin of the left subclavian artery. Associated findings corresponding to isthmus hypoplasia, poststenotic dilation, and diminished systolic pulsations within the descending aorta serve to verify the presence of a major coarctation. Color-flow Doppler assists in localizing the site of obstruction and is particularly useful in circumstances where 2-D imaging is troublesome or inconclusive. Doppler echocardiography can assist in figuring out the hemodynamic severity of a coarctation. A continuous-wave Doppler examine from the suprasternal window will detect high-flow velocity throughout the stenosis. A peak instantaneous pressure gradient could also be decided from the maximal move velocity using the modified Bernoulli equation. The Doppler-flow show throughout the coarctation often demonstrates a pattern of diastolic runoff, particularly in patients with a extreme stenosis or with a strong collateral circulation. A corrected gradient is obtained by subtracting Cardiac catheterization can serve both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes in patients with a coarctation. Diagnostic cardiac catheterization is pointless if noninvasive analysis clearly delineates the lesions which are current. If essential clinical questions remain regarding the character and severity of a coarctation or potential associated intracardiac lesions, a diagnostic cardiac catheterization may be carried out. The aims of a diagnostic cardiac catheterization in a patient with coarctation are to outline the anatomy and severity of the coarctation, the nature of the arterial collateral circulation, the presence and severity of associated lesions, left ventricular function, and pulmonary artery stress and resistance. The hemodynamic severity of a coarctation often is assessed by the magnitude of the systolic pressure gradient. Coarctation causes an elevated systolic strain and pulse pressure throughout the ascending aorta and a diminished systolic pressure and pulse stress within the descending aorta. In a baby with an isolated coarctation and a standard cardiac output, a systolic gradient <20 mm Hg is commonly indicative of mild coarctation. However, strain gradient alone may underestimate the hemodynamic significance of a coarctation. The strain gradient may be diminished with left ventricular dysfunction and low cardiac output, by a big patent ductus arteriosus, by a number of left-sided obstructive lesions in series, or by a well-developed collateral circulation that decompresses the ascending aorta. The anatomy of the coarctation and collateral circulation generally is greatest imaged by an ascending aortogram filmed in the anteroposterior and straight lateral projections. Note the diastolic runoff sample according to a pressure gradient throughout diastole.

100 caps gasex sale
The weak point is unique among the many frequent muscular dystrophies gastritis or appendicitis discount 100 caps gasex overnight delivery, affecting distal equal to or larger than proximal muscle tissue diet of gastritis patient discount 100caps gasex fast delivery. Patients can also have frontal baldness gastritis fatigue generic 100caps gasex with visa, diabetes, and incessantly, infertility (97). When Steinert (98) described the disease, he noted that sufferers often had a slow pulse rate. Cardiac ventricular diastolic and systolic duration in youngsters with coronary heart failure secondary to idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Survival in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: improvements in life expectancy since 1967 and the impact of house nocturnal air flow. Observations of the cardiovascular involvement, together with the cardiac conduction system, in progressive muscular dystrophy. The incidents of extreme anesthetic problems in sufferers and households with progressive muscular dystrophy of the Duchenne and Becker sorts [in German]. Electrocardiographic abnormalities and arrhythmias are strongly associated with the event of cardiomyopathy in muscular dystrophy. Echocardiographic and electrocardiographic findings of cardiomyopathy in Duchenne and Becker-Kiener muscular dystrophies. Genetic predictors and reworking of dilated cardiomyopathy in muscular dystrophy. Sequential changes in cardiac construction and function in sufferers with Duchenne kind muscular dystrophy: a twodimensional echocardiographic study. The relationship between medical stage, prognosis and myocardial injury in patients with Duchenne-type muscular dystrophy: five-year follow-up examine. Prevalence and distribution of regional scar in dysfunctional myocardial segments in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Circumferential Strain Analysis IdentifiesStrata of Cardiomyopathy in duchenne Muscular dystrophy. Occult Cardiac Contractile Dysfunction in Dystrophin-Deficient Children Revealed by Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Strain Imaging. Clinical-molecular correlation in 104 delicate X-linked muscular dystrophy patients: characterization of subclinical phenotypes. Evidence for a dystrophin missense mutation as a explanation for X-linked dilated cardiomyopathy. Brief report: deletion of the dystrophin muscle-promoter region related to X-linked dilated cardiomyopathy. Cardiac involvement in myotonic dystrophy, Becker muscular dystrophy and mitochondrial myopathy: a five-year follow-up. Clinical and molecular genetic spectrum of autosomal dominant Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy as a outcome of mutations of the lamin AlC gene. Novellamin AlC mutations in two families with dilated cardiomyopathy and conduction system illness. Cardiac features of EmeryDreifuss muscular dystrophy caused by lamin AlC gene mutations. Advances within the molecular genetics of the limbgirdle sort of autosomal recessive progressive muscular dystrophy. Natural historical past of cardiomyopathy in Duchenne muscular dystrophy and the effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor and/or P-blocker. Early remedy with lisinopril and spironolactone preserves cardiac and skeletal muscle in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy mice. The Efficacyand Safety of the Novel Aldosterone Antagonist Eplerenone in Children with Hypertension: a Randomized, Double-Blind, Dose-Response Study. Outpatient steady inotrope infusion as an adjunct to heart failure remedy in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Idebenone as a novel, therapeutic strategy for Duchenne muscular dystrophy: outcomes from a 12 month, double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial. Abnormalities of the electrocardiogram in female carriers of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. The heart in Becker muscular dystrophy, fascioscapulohumeral dystrophy and Bethlem myopathy. Evolution of cardiac abnormalities in Becker muscular dystrophy over a 13-year period. Analysis of dystrophin deletion mutations predicts age of cardiomyopathy onset in becker muscular dystrophy. Becker muscular dystrophy-related cardiomyopathy: a favorable response to medical remedy. Left ventricular synchronization by biventricular pacing in Becker muscular dystrophy as assessed by tissue Doppler imaging. The principal symptoms and associated features of the acute part of the syndrome are proven in Tables 59. Despite latest increases in incidence, current estimates of mortality within the United States are decrease (0% to 0. The threat of incidence in twins may be as a lot as 100-fold larger than in the general inhabitants (14,15). An infectious trigger is suggested by the epidemiologic traits of this syndrome, particularly its tendency to goal younger youngsters, time/place clustering, a predilection for winter and spring months, and epidemic cycles every three years (observed most clearly through the Nineteen Seventies and 1980s). Indeed, numerous infectious brokers have been proposed including rickettsia (17), propionibacterium (18), streptococci or their merchandise (19), home mud mite antigen (20), and retrovirus (21). There is elevated production of immunoglobulins, including circulating antiendothelial antibodies (25). Pro inflammatory cytokines appear to render the vascular endothelium prone to lysis by antibodies (27). Activated vascular endothelium expresses inflammatory antigens similar to intercellular adhesion molecules. Young infants have the very best price of coronary artery aneurysm formation and often current with incomplete clinical criteria. Children older than age 8 years also have the next fee of coronary involvement (8-10). The charges of coronary artery aneurysm based on race/ethnicity have been estimated using administrative data; charges were highest in Hispanics (5. Diagnosis, treatment, disease: A assertion for well being of Kawasaki management of Kawasaki from the Committee Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association. Various mitogenic elements such as vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived development factors are expressed during acute and subacute phases. Various strains of Staphylococcus and Streptococcus have been proposed as the inciting immune perturbation, with toxins appearing as super antigens recruiting T lymphocytes bearingVj32 and Vj38 receptors (30). The identical investigators demonstrated immunohistochemical evidence of antigens within the respiratory epithelium and macrophages that react with artificial IgA antibodies genetically engineered from these plasma cells (32).
Safe 100 caps gasex
If the hemodynamics enable gastritis lower back pain discount gasex 100 caps on line, the fenestration may be closed in the early postoperative period (33) or later at cardiac catheterization (34) gastritis diarrhea buy discount gasex 100 caps on line. Before the widespread use of the modified Fontan procedure gastritis diet òâ cheap gasex 100caps overnight delivery, the likelihood of a affected person born with tricuspid atresia surviving into younger adulthood was still fairly low (-50%). Patients who endure full separation of the pulmonary and systemic venous returns by a modified Fontan process have widely varying outcomes, depending on details of the preoperative hemodynamic standing (35-37). The general mortality fee of sufferers present process the Fontan process in latest collection is between 7% and 11 % (38-40); nevertheless, a lot of the bigger sequence embrace patients with many forms of single-ventricle physiology, and so these results must be reviewed rigorously for the result of patients with tricuspid atresia. Although some sufferers undergoing a modified Fontan process have excellent outcomes, others develop main medical issues, including growth of collateral (both arterial and venous) vessels. If the quantity of shunting is substantial, leading to important systemic desaturation, a few of these channels could be occluded using catheterization strategies. Unfortunately, other channels are prone to develop except the underlying physiology is corrected. On the other hand, systemic arterial collateral vessels may develop from the descending aorta. These collaterals talk with the pulmonary arterial tree, and the circulate from these vessels competes with the low-pressure pulmonary blood flow created by the modified Fontan process. The marked change in proper atrial strain and subsequent disturbance in lymphatic drainage and hydrostatic stress, nevertheless, are more doubtless to be involved. Various treatment modalities, including administration of corticosteroids or heparin, have been tried with varying success (44-46). Because of hypoalbuminemia, administration of parenteral albumin and a food plan including medium-chain triglycerides could also be helpful. Causes for this decreased response include lack of a right ventricle, depressed left ventricular operate, impaired chronotropic response, conduit obstruction, or irregular pulmonary vascular resistance. Because of the compromise in right coronary heart circulate even in the best results, most cardiologists now suggest anticoagulation. Some investigators differentiate tricuspid valvar stenosis from hypoplasia of the valve (50). In the former condition, the annulus may be comparatively massive, but the leaflets are thickened with commissural fusion and shortened chordae tendineae. In the latter situation, the valve annulus is small, and the leaflets and chordae may be diminutive but otherwise normal. Careful ultrasound evaluation of the pulmonary valve is likely to differentiate between useful and anatomic atresia of the right ventricular outflow tract (55,56). Right ventricular systolic strain may be elevated, however within the case of severe insufficiency, it may be normal. The degree of pulmonary artery opacification will depend on whether the right ventricle can generate sufficient ahead flow to open the pulmonary valve within the face of elevated neonatal pulmonary vascular resistance. Resolution of neonatal tricuspid insufficiency has been described, presumably in sufferers with comparatively normal tricuspid valve structure and insufficiency owing to papillary muscle dysfunction (54). For sufferers who survive the new child interval and reside into childhood, adolescence, or adulthood, the surgical choices are likely to be higher, with a better likelihood of success. Some investigators have suggested, subsequently, that isolated tricuspid stenosis is merely a light type of tricuspid atresia. Differentiating between the 2 is important as a end result of better choices for surgical intervention may exist in patients with tricuspid stenosis in contrast with those with tricuspid atresia. The first description in a living affected person reported clinical and catheterization knowledge and reviewed beforehand revealed stories (53). Infants requiring intervention are more doubtless to have more extreme lesions, and the results are prone to be worse (49). Older sufferers can be expected to fare better, with commissurotomy or valve substitute being the main choice. Various anatomic abnormalities of the tricuspid valve have been described, accounting for a few of these circumstances. Tricuspid valve insufficiency also could additionally be related to different lesions, particularly severe stenosis or atresia of the proper ventricular outflow tract. In this case, nevertheless, the tricuspid insufficiency, in all probability, is a secondary phenomenon. Occasionally, tricuspid valve insufficiency might occur with a structurally regular valve within the absence of related lesions. Anatomic abnormalities resulting in tricuspid valve insufficiency have been nicely described. In some cases, one or more of the valve leaflets may present nodular thickening with shortened chordae tendineae and hypoplastic or absent papillary muscular tissues (55,56). Interestingly, related nodules are often also found on the mitral valve, though mitral insufficiency is rare. Other structural abnormalities of the tricuspid valve have been described, together with an isolated cleft of a valve leaflet and absence of valve tissue altogether with a relatively regular valve annulus (unguarded tricuspid orifice). Age at presentation clearly depends on several components, crucial of which is the diploma of valve dysfunction, which can be exaggerated in a newborn in the presence of elevated pulmonary vascular resistance and notably following a sophisticated perinatal course. In neonates and infants with severe tricuspid insufficiency, cyanosis and medical findings of congestive cardiac failure appear early. Cardiac examination includes a pansystolic murmur loudest on the left lower sternal border, usually with a precordial thrill. The chest radiograph is likely to show marked cardiomegaly with diminished pulmonary vascular markings. Uhl anomaly, because it has come to be known, is extraordinarily rare, and by 1979, <20 circumstances had been reported, each individually as a case report (59). Some investigators have advised that this situation is expounded to different conditions that have an result on the proper ventricular myocardium, such as arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia (60). The typical anatomic findings of Uhl anomaly have been described on prenatal ultrasound examination (61). Ages at postnatal presentation ranged between 1 day and 57 years, with equal gender distribution. Most patients have been clinically cyanotic, and, except for the presence of an atrial septal defect or patent foramen ovale, different related congenital heart defects were rare. At physical examination, along with cyanosis, hepatomegaly is commonly present as properly as jugular venous distension with a dominant "a" wave. Surprisingly, in view of gross right ventricular dilation found at post-mortem, the precordium normally is described as being quiet, and peripheral pulses typically are diminished in amplitude. Cardiac auscultation normally reveals a decrease in the depth of the guts tones, particularly the first coronary heart sound. A typical pansystolic murmur of tricuspid insufficiency may be current, however patients might have other nonspecific murmurs or certainly no murmur at all. The chest radiograph demonstrates cardiomegaly, usually of spectacular degree, and regular to diminished pulmonary vascularity, typically resulting in the mistaken prognosis of Ebstein anomaly of the tricuspid valve. Echocardiography demonstrates marked dilation of the right-sided cardiac chambers. Although detailed echocardiographic investigation of Uhl anomaly using present-day instrumentation has not been described, an essential finding is the presence of the tricuspid valve leaflets arising appropriately from the annulus, differentiating this lesion from Ebstein anomaly.
References
- Choyce A, Avidan MS, Patel C, et al: Comparison of laryngeal mask and intubating laryngeal mask insertion by the naive intubator. Br J Anaesth 84:103, 2000.
- Blute ML, Amling CL, Bryant SC, et al: Management and extended outcome of patients with synchronous bilateral solid renal neoplasms in the absence of von Hippel-Lindau disease, Mayo Clin Proc 75:1020n1026, 2000.
- Jonnavithula, N., Pisapati, M.V., Durga, P., Krishnamurthy, V., Chilumu, R., Reddy, B. Efficacy of peritubal local anesthetic infiltration in alleviating postoperative pain in percutaneous nephrolithotomy. J Endourol 2009;23:857-860.
- Tadokoro Y, Ema H, Okano M, et al. De novo DNA methyltransferase is essential for self-renewal, but not for differentiation, in hematopoietic stem cells. J Exp Med 2007;204(4):715-722.
- Grocela JA, McDougal WS: Ammonium transport in the intestine chronically exposed to urine: is it reduced over time?, Urology 54:373n376, 1999.
- Cheuk DKL, Yeung WF, Chung KF, Wong V. Acupuncture for insomnia. Coch Database Syst Rev 2007;3:CD00Chen ML, Lin LC, Wu SC, Lin JG. The effectiveness of acupressure in improving the quality of sleep of institutionalized residents. J Gerontol 1999;54:389-94.

